random.triangular(low, high [, mode])
The random.triangular function returns a random number N drawn from a triangular distribution such that low <= N <= high, with the mode specified in the third argument, mode.
If the mode argument is not specified, it defaults to the value (low + high) / 2, that is, the value located at the midpoint of the range considered.
- low: Lower limit of the range from which to extract the random number.
- high: Upper limit of the range from which to extract the random number.
- mode: Optional argument. Mode of the distribution.
The random.triangular function returns a real number.
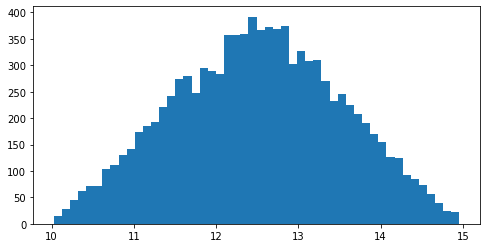
We can generate a random number in the range [10.0, 15.0] extracted from a triangular distribution with a default mode equal to 12.5 with the following code:
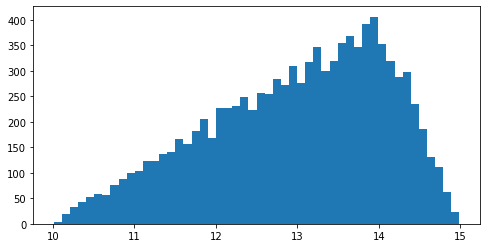
We could repeat the previous example forcing a mode equal to 14 with the following code:
To confirm the distribution from which the random numbers are extracted we can generate 10 thousand random numbers in the range [10.0, 15.0] with default mode and show its histogram:
plt.hist([random.triangular(10, 15) for i in range(10000)], bins = 50)
plt.show()