Unsupervised learning algorithms are an important tool in the field of machine learning, and are used to make predictions or decisions based on data. Unlike supervised learning algorithms, which are trained using labeled data, unsupervised learning algorithms do not have labeled training data. Instead, they use the inherent structure of the data to learn and make predictions.
A common example of an unsupervised learning algorithm is clustering, which is used to divide a set of data into groups or clusters based on the similarity between the data:
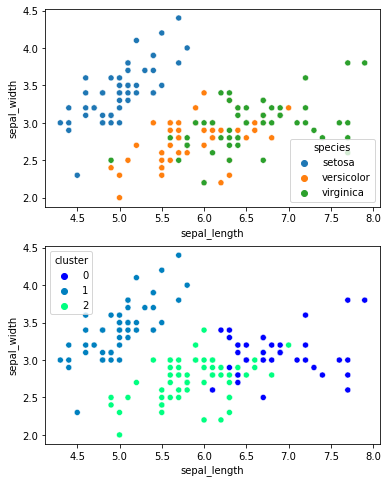
Another example is dimensionality reduction, which is used to reduce the number of features in a set of data while maintaining the important information.
In addition to clustering and dimensionality reduction, unsupervised learning algorithms can also be used to detect patterns or trends in the data and to perform principal component analysis. Unsupervised learning algorithms are also used in anomaly detection applications and in product recommendation.
Overall, unsupervised learning algorithms are a useful tool for making predictions or discovering patterns in unlabeled data. However, because they do not use labeled training data, they may be less accurate than supervised learning algorithms in some applications. Despite these potential drawbacks, unsupervised learning algorithms remain an important tool in machine learning and have a wide range of practical applications.