The STDEVX.S function returns the standard deviation of a sample of the population drawn from a table to whose rows a certain expression is applied.
STDEVX.S(
table,
expression
)
- table: Table containing the rows for which the expression will be evaluated.
- expression: Expression to evaluate for each row of the table.
The STDEVX.S function returns a real number.
The function evaluates the expression included as the second argument for each of the rows of the indicated table, returning the standard deviation assuming that the table refers to a sample of the population. If the table represents the total population, the STDEVX.P function should be used.
The STDEVX.S function uses the following formula:
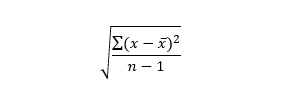
...where x̃ is the mean value of x for the sample population and n is the size of the population. The use of n-1 instead of n is known as the Bessel's correction.
Empty rows are ignored in the calculation. If there are less than two non-empty rows, the function returns an error.
Suppose we have the following table showing a list of products and their sale price:

Assuming that the data shown is a sample of the population, we can calculate the standard deviation of the prices using the following measure:
Desviación estándar = STDEVX.S(Ventas, Ventas[Precio])
If we take this measure to a card-type display, we obtain the following result:

If, instead of a list of products and prices, we had a list of sales including the quantity sold and the unit price of each sale:

...we could calculate the standard deviation of the invoiced figures (that is, of the product of the quantity and the unit price) -assuming that they represent a sample of the population- with the following measure:
Desviación estándar = STDEVX.S(Ventas, Ventas[Cantidad] * Ventas[Precio])
...which, taken to a card-like display, returns the following result:
