The TAN function returns the tangent of the angle passed as an argument.
TAN(
<value>
)
- value: Angle in radians whose tangent you want to calculate.
The TAN function returns a real number corresponding to the tangent of the indicated angle.
This function requires that the angle it receives as a parameter be expressed in radians. If the available angle is in sexagesimal degrees, it will have to be multiplied by PI()/180 or use the RADIANS function to convert it to radians.
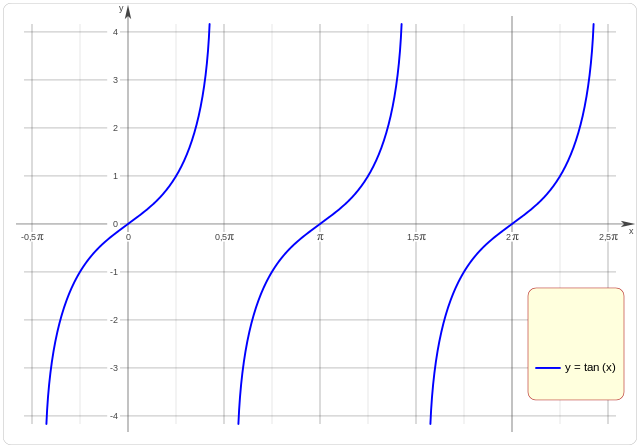
From Dnu72 - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Link
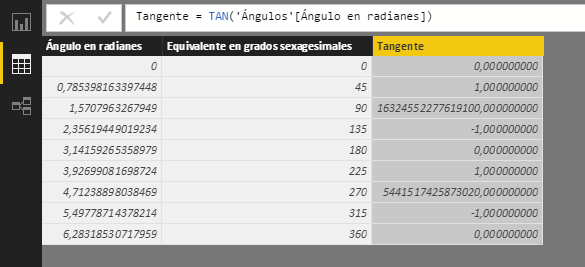
The behavior of this function around points with vertical asymptotes is not reliable. Thus, as can be seen in this example, the 270º tangent (3*PI()/2):

...is a number that tends to infinity, but with a positive sign, which is an approximation to the limit from its left (and not from its right, as might be expected).
The following example shows the tangent of various angles: